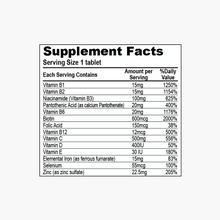
- 90 Tablets
- Supports Immune System.
- Promotes cellular energy production.
- Supports daily body needs.
- Comparable to Abbots SurbexZ but with additional Iron, Selenium, Biotin, & Vitamin D.
Additional Information
Zinc:
Zinc is used for treatment and prevention of zinc deficiency and its consequences, including stunted growth and acute diarrhea in children, and slow wound healing. Zinc is needed for the proper growth and maintenance of the human body. It is found in several systems and biological reactions, and it is needed for immune function, wound healing, blood clotting, thyroid function, and much more. Meats, seafood, dairy products, nuts, legumes, and whole grains offer relatively high levels of zinc.
It is also used for boosting the immune system, treating the common cold and recurrent ear infections, and preventing lower respiratory infections. It is also used for malaria and other diseases caused by parasites.
Some people use zinc for an eye disease called macular degeneration, for night blindness, and for cataracts. It is also used for asthma; diabetes; high blood pressure; acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS); and skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and acne.
Other uses include treating attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), blunted sense of taste (hypogeusia), ringing in the ears (tinnitus), severe head injuries, Crohn’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, Down syndrome, Hansen’s disease, ulcerative colitis, peptic ulcers and promoting weight gain in people with eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa.
Some people use zinc for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), male infertility, erectile dysfunction (ED), weak bones (osteoporosis), rheumatoid arthritis, and muscle cramps associated with liver disease. It is also used for sickle cell disease and inherited disorders such as acrodermatitis enteropathica, thalassemia, and Wilson’s disease.
Some athletes use zinc for improving athletic performance and strength.
Iron:
Iron is vital for the production of hemoglobin, the part of red blood cells that ferries oxygen to cells. Nearly two-thirds of the body’s iron is found in hemoglobin, which explains iron’s key role in promoting life and supporting health. Smaller amounts of iron are found in myoglobin, a protein that’s responsible for transporting oxygen and storing it on a short-term basis within the muscles. Iron is critical for regulating cell growth and replication, as well as for skin repair. It supports your immune system and is required for normal brain and nervous system function.
It is an essential component of dozens of enzymes – proteins that initiate chemical reactions in the body – including those involved in energy production and for making DNA, the cells’ blueprint for reproduction. Iron supports your immune system, too. It is necessary to produce certain cells to make the enzymes that kill the germs that can make you ill.
Iron is required for normal brain and nervous system function at the cellular level and beyond. Neurotransmitters, the compounds that allow nerve cells to communicate, depend on iron, as does myelin, the protective sheath that surrounds and insulates nerve fibers. According to the USDA’s 2010 dietary guidelines for Americans, iron is one of the nutrients of concern for women in their childbearing years. A large number of females, who are capable of becoming pregnant, including adolescent girls, are deficient in iron. In fact, iron deficiency is the most common nutrient shortfall in the United States.
About 15% of the body's iron is stored for future needs and mobilized when dietary intake is inadequate. When iron levels in the blood are low for a prolonged period of time, there is insufficient iron available to support normal red blood cell production, which may result in iron-deficiency anemia. Iron deficiency can limit oxygen delivery and the production of enzymes that rely on iron to function properly, including those involved in energy production.
Insufficient dietary iron is often the culprit in iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia, but chronic bleeding or a large blood loss may also be to blame. In the absence of bleeding, including menstruation, or pregnancy, the body normally loses only tiny amounts of iron every day, so a constant loss of even a very small amount of blood may result in iron deficiency with time.
Inadequate iron intake resulting in deficiency can lead to health complications. Symptoms include:
- Fatigue;
- Muscle weakness;
- Lack of stamina;
- Light-headedness;
- Loss of libido;
- Sluggish immune system.
These symptoms are associated with poor oxygenation of the body, both in muscles and in several organs such as the brain, heart, kidneys and lungs. Scientists have also observed that a lack of iron can lead to learning difficulties and poor concentration. This is why supplementing with iron may help improve cognitive ability and prevent heart failure.
You can get iron from Wheat Cereal, Bran Cereal, Instant Oatmeal, Mussels.
Biotin:
Biotin supports healthy skin, healthy hair, brittle nails, nerves, digestive tract, metabolism, cells and other conditions.
- PROMOTES HEALTHY HAIR, SKIN & NAILS – Restore the health of your hair, radiance of your skin and strength of your nails with XGen Biotin, an important B vitamin that has long been known as a key element in maintaining healthy hair, skin and nails.
- INCREASE ENGERY – Biotin, a B vitamin also known as vitamin H or B7 is water soluble and helps support the metabolism and assists in the conversion of food (fats & carbohydrates) into energy.
Biotin supplements have also been studied as a treatment for decreased insulin resistance and nerve symptoms related to type 2 diabetes, hepatitis, hair loss, and depression.
Biotin is widely distributed in foods. However, data on the actual biotin content of foods is limited and varies significantly. To ensure you get the biotin you need, eat a well - balanced diet with a variety of foods.
Selenium:
Selenium is a powerful mineral that is essential for the proper functioning of the body. For starters, it plays a critical role in metabolism and thyroid function. It also helps protect the body from damage caused by oxidative stress.
Selenium is an essential trace mineral that assists with cognitive function and fertility. Selenium may help prevent cardiovascular disease, thyroid problems, cognitive decline, which means disorders related to thinking, cancer, and others.
Vitamin D3:
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that helps your body absorb calcium and phosphorus. Having the right amount of vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus is important for building and keeping strong bones.
Your body must have vitamin D to absorb calcium and promote bone growth. Too little vitamin D results in soft bones in children (rickets) and fragile, misshapen bones in adults (osteomalacia). You also need vitamin D for other important body functions.
In its active form as calcitriol, vitamin D contributes to skin cell growth, repair, and metabolism. It optimizes the skin's immune system and helps destroy free radicals that can cause premature aging. While the body can produce vitamin D on its own through sun exposure, too much sun accelerates skin aging.
Here are 8 signs and symptoms of vitamin D deficiency.
- Getting Sick or Infected Often. ...
- Fatigue and Tiredness. ...
- Bone and Back Pain. ...
- Depression. ...
- Impaired Wound Healing. ...
- Bone Loss. ...
- Hair Loss. ...
- Muscle Pain.
Zinc References:
http://www.webmd.com/vitamins-supplements/ingredientmono-982-zinc.aspx?activeingredientid=982